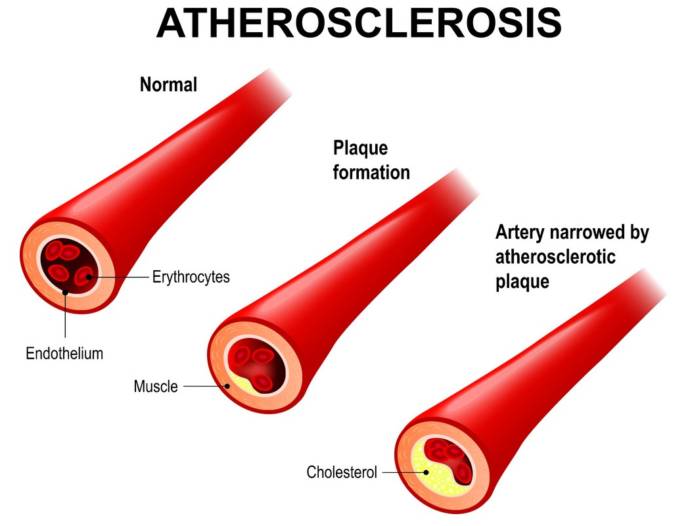
Atherosclerosis is the condition characterized by the narrowing of arteries due to the plaque. The symptoms of atherosclerosis occur due to reduced blood flow in the related tissue. The symptoms of atherosclerosis include chest pain, dizziness, nausea, vomiting, and pain and numbness in body parts. Diagnosis is done through blood tests, imaging techniques, and electrocardiogram.
Types
Atherosclerosis is divided into the following types on the basis of the type of plaque formation:
- a) Fibro-fatty plaque: This type of plaque generally comprises of the fatty acids and the fibrous tissue. There is a fibrous matter on the plaque and the core comprises of lipids. These plaques, when burst, cause severe damage to the arteries.
- b) Fibrous plaque: This type of plaque predominantly comprises collagen fibers. Other components of these plaques include calcium depositions and very few cells containing lipids.
Atherosclerosis can also be divided on the basis of the site at which the plaque has been formed:
- a) Coronary artery atherosclerosis: When the plaque is formed in the artery supplying blood to the heart, it is known as Coronary artery atherosclerosis.
- b) Peripheral atherosclerosis: This type of atherosclerosis is caused when the plaque is present in the peripheral vascular system.
- c) Carotid atherosclerosis: This atherosclerosis develops when the plaque occurs in the carotid artery which carries blood to the brain tissues.
Causes
- High cholesterol: High blood cholesterol level is one of the main reasons for atherosclerosis. The excess cholesterol present in the blood is deposited on the walls of the arteries. This build-up of cholesterol increases with time and may block the arteries.
- Diet: Diet also plays an important role in the development of atherosclerosis. A low-fat diet is advised to the patients who have a high risk for atherosclerosis.
- Aging: As the age of the person increases, the synthesis of nitric oxide decreases. Nitric oxide is believed to be an important substance for reducing the development of atherosclerosis.
- Smoking: Smoking increases the level of bad cholesterol and also causes hypertension. Further, nicotine and carbon monoxide present in cigarette damages endothelium.
- Diabetes: High blood sugar increases the inflammation and reduces the flow of blood leading to atherosclerosis.
- Cardiovascular disease: High blood pressure increases the risk of atherosclerosis. Untreated high blood pressure causes scarring and hardening of the vessels.
- Concurrent medical condition: Various inflammatory medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis also causes atherosclerosis.
Symptoms
The symptoms of atherosclerosis depend upon the type of artery that has been affected. Following are the general symptoms associated with atherosclerosis:
- Chest pain
- Pain and weakness in muscles
- Abdominal pain
- Pain in hand, shoulders, and back.
- Dizziness
- Nausea
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Confusion
- Neurological disorder
- Perspiration
- Lightheadedness
- A headache
- Vision changes
- Numbness
How to diagnose
Following are the diagnostic methods used by the physicians for diagnosing atherosclerosis:
- Angiography: Angiography is the technique to identify the blockage or any plaque inside the artery. In this process, a dye is injected in the artery and through X-ray, the flow of dye is monitored. On the basis of the flow of dye, atherosclerosis is identified.
- Stress testing: This method is used to identify the presence of atherosclerosis in the coronary artery. The patient is subjected to exercise and on the basis of change in pulse and blood pressure, diagnosis of the disease is done.
- Imaging techniques: various imaging techniques are used to evaluate the health of arteries. Computed tomography scan is used to analyze the hardening of the arteries. Chest X-ray is also done to identify any anomaly in heart and the abdominal region.
- Blood test: Blood test is done to check the level of cholesterol, both good and bad, triglycerides and level of sugar.
- Electrocardiogram: This method is used to evaluate the electrical health of the heart. This shows how the electrical impulses are transmitted and also evaluates the functional capability of cardiac muscles.
- Echocardiogram: This helps to identify any abnormality in the valves of the heart and its chambers.
Risk neglecting Atherosclerosis
- Cardiac complications: Atherosclerosis in the coronary artery may lead to cardiac arrest. It also results in cardiac arrhythmia. The patient may experience severe chest pain due to the heart attack.
- Stroke: When the atherosclerosis of the brain is not managed, it may lead to stroke. Stroke is a life-threatening condition which may result in coma or lifelong disability.
- Erectile dysfunction: Atherosclerosis may also lead to erectile dysfunction due to reduced blood flow in the genital area.
- Death: Untreated atherosclerosis may also cause death either due to cardiac arrest or stroke.
- Claudication in vessels: Atherosclerosis may also cause reduced blood flow in the peripheral organs including hand and legs. This causes claudication and pain. The patient feels difficulty in moving and performing routine tasks.
Stages
The progression of atherosclerosis is divided into the following stages:
- Stage I: In this stage, the inner layer of the vessels gets damaged due to high blood pressure or aging.
- Stage II: In this stage, the inflammatory response is initiated, and the white blood cells flow to the damaged site. Cholesterol began to deposit at this spot. This deposition is known as atheroma.
- Stage III: Elasticity of the artery is lost due to further deposition of calcium and fibroid tissue. This leads to complete plaque formation.
Foods
- Fatty fish containing omega-3 fatty acids
- Turmeric to reduce inflammation
- Almonds
- Watermelon
- Avocado
- Whole Grain
- Beans and legumes
- Essential oils such as chamomile
Prevention tips
- Take supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids, Coq10, and magnesium.
- Exercise regularly.
- Reduce stress levels.
- Avoid high fatty meals.
- Take good sleep.
- Avoid anger, depression, anxiety, and overeating.
- Manage diabetes, blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Control weight.
- Avoid smoking.
- Take a healthy diet.
When to see a doctor
Call your doctor if:
- You have chest pain.
- You have a feeling of nausea and vomiting.
- You experience dizziness.
- You have trouble breathing.
- You have pain or numbness in any part of the body.