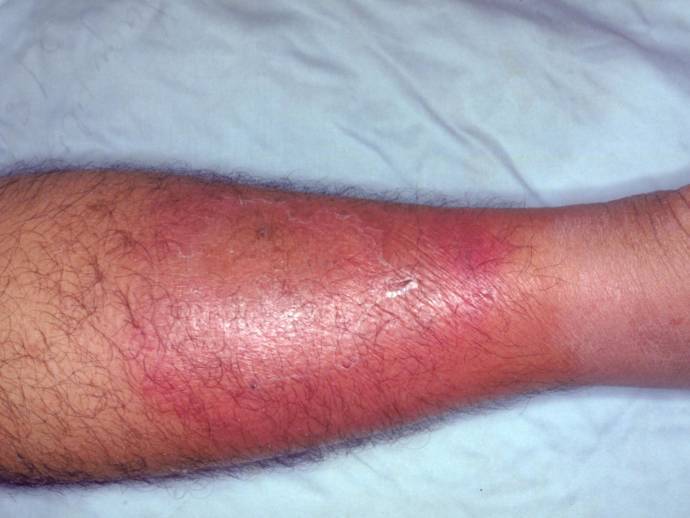
Cellulitis is the condition caused due to the infection of the skin and deeper tissues. It is caused due to bruising and cutting of the skin which allows the bacteria to enter. Diagnosis is generally done through physical evaluation. Symptoms include pain, fever, redness, and inflammation. Complications may lead to endocarditis, meningitis, and sepsis.
Types
Cellulitis can be classified on the basis of parts that gets affected by the infection. Following are the types of cellulitis:
- Facial cellulitis: This type of cellulitis affects tongue, lips, and face. The symptoms include redness, swelling, and pain on the affected organ. This is also accompanied by chills, fever, and irritability. The facial skin becomes tender and warm to touch.
- Periorbital cellulitis: This type of cellulitis is most commonly found in children and infants. This infection affects the eye, eyelids, and tissues around the eyes. This is caused due to the scratch or any injury around the eyes which causes infections. This type of cellulitis is also known as preseptal cellulitis.
- Breast cellulitis: Breast and the surrounding tissues such as shoulders, and arms are affected by this form of cellulitis. The affected tissues are warm and swollen.
- Perianal cellulitis: Characterized by the presence of bloody stools and reddened anal orifice, this cellulitis affects the anal region of the body. Males are significantly at higher risk of developing this form of cellulitis as compared to female.
- Cellulitis of the Extremities: This type of cellulitis affects the extremities of the body including arms, hands, and legs.
Causes
- Infections due to cuts and bruises
- Post-surgical infection
- Medical history of skin diseases such as eczema or psoriasis
- Medical implants which may cause infection
- Chronic unmanaged infection that has spread to skin and soft tissues
- Boone infections
Symptoms
Following are the symptoms of cellulitis:
- Pain
- Inflammation
- Redness and tender to touch
- Fever and malaise
- Abscess
- Tight and glossy skin
- Drowsiness
- Fatigue
Ways to diagnose
Diagnosis of the disease can be done through the following methods:
- Physical examination: The physician may confirm the presence of cellulitis on the basis of the characteristic feature found during physical examination of the wound. The patient suffers from fever and malaise. Other symptoms related to cellulitis presented by the patients include bullae, dermal necrosis, and superficial hemorrhage. Erythema is well marked and spreads rapidly.
- Blood tests: After the physical examination, the doctor may advise the patient to undergo various blood tests which confirms the presence of infection in the blood. As with all the infections, the blood test reveals increased leucocyte count and raised C-reactive protein. In some patients, the culture of the local lesion can be done either through needle aspiration or by taking a swab.
Risks if neglect
If the cellulitis is not treated properly, it may lead to the following complications:
- Endocarditis: The infection of the skin may reach to the heart and cause endocarditis. This may interfere with the functioning of the heart and may lead to life-threatening consequences such as arrhythmia and heart failure.
- Bone infection: Infection from the deeper tissue may spread to the bones and may cause osteomyelitis.
- Brain infections: The infection from the skin and deeper tissues may attack the membrane of the brain and may lead to meningitis.
- Sepsis: If the cellulitis is not treated at an early stage, it may lead to sepsis, i.e. the infection of the blood. Risk of spreading the infection to other vital organs is significantly increased. Sepsis may progress into septic shock.
Stages
Cellulitis is divided into various stages on the basis of the severity of symptoms. The classification is done to provide more rationale treatment to the patient. These stages are:
- Class 1: The patients with class 1 cellulitis have mild symptoms. The patient can generally be treated as an outpatient with antibiotics. The patient does not present any symptoms of systemic toxicity and no uncontrolled comorbidities are present in this the patient suffering from class 1 cellulitis.
- Class 2: The patients suffering from class 2 cellulitis presents the comorbidities such as chronic venous insufficiency or peripheral vascular disease. These comorbid conditions may cause a delay in healing of infection. The patient may or may not presents the symptoms of systemic infection.
- Class 3: There is the severity of peripheral vascular disease in the patients suffering from class 3 cellulitis. The patient presents the symptoms of systemic infection such as hypotension, confusion, and rapid heart rate.
- Class 4: This is the severest form of cellulitis. The patient of class 4 cellulitis has sepsis and if immediate medical intervention is not done, it may lead to septic shock.
Foods to eat and avoid
Foods to eat:
- Fish rich in omega-3 fatty acids.
- Pumpkin seeds
- Garlic
- Turmeric
- Pineapple
- Citrus fruits
- Tea tree oil
- Yogurt
Foods to avoid:
- Fried foods
- Salty foods
- Cheese
- Butter
- Margarine
- Processed Meats
Prevention tips
- Maintain hygienic habits.
- Take care of the wounds properly.
- Avoid smoking.
- Limit the intake of alcohol.
- Follow a healthy lifestyle.
- Protect your skin from injury.
- Limit the amount of sugar intake.
When to see a doctor
Call your doctor if:
- If you have any cut or bruising mark on the skin that becomes reddened.
- If your condition worsens along with fever and chills.
- If your condition does not become better even after taking medications.
- If any other symptoms that make you concerned.
Do’s & Don’ts
Do’s
- Do take protective measures to avoid any skin injury.
- Adhere to the prescription and take medicines as prescribed.
- Keep moving your leg in case of swelling to avoid clotting.
- Book an appointment with your healthcare professional if your condition worsens.
- Do get information about the disease.
- Apply antiseptic immediately on any cut marks on the skin after cleaning it.
Don’ts
- Avoid swimming if you have an open wound.
- Do not skip your dose.
- Do not engage in strenuous activities as this may further worsen your health.
- Avoid vigorous physical activity until your pain subsides.
- Do not ignore any cut marks on the skin.
Risks for specific people
People with skin conditions such as eczema, and dermatitis. People with compromised immune system and history of skin disorders are significantly at higher risk. Risk factor for cellulitis also includes obesity and lymphedema.