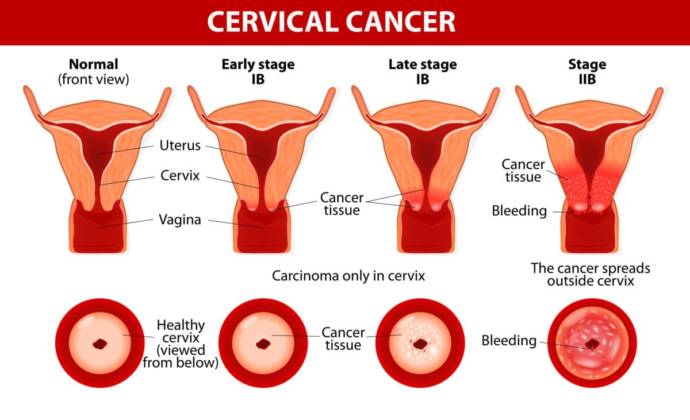
Cervical cancer is the abnormal growth of cells inside the cervix, which has the potential to metastasize to other parts of the body. Most common cervical cancer is squamous cancer. Symptoms include heavy bleeding, vaginal dryness, and vaginal discharge. Causative factors include Human papillomavirus infection, unprotected sex, chlamydia infection, and weak immune system.
Types
Following are the different types of cervical cancer:
- Squamous cell cancer: This type of cancer is found in the outer surface of the cervix as this part is mainly composed of squamous cells. This is the most common cervical cancer.
- Adenocarcinoma: Various glandular cells are scattered inside the cervix. The function of these cells is to produce mucus. Adenocarcinoma is the cancer of these glandular cells. These cells are present from the cervix to the womb.
- Adenosquamous carcinoma: This type of cancer is not common and is characterized by the presence of both squamous cell cancer as well as adenocarcinoma.
- Small cell cervical cancer: This is the highly spreadable form of cancer which rapidly spreads to lymph nodes or other body areas.
- Miscellaneous cancer: Various other rare types of cancers is found in the cervix. These cancers include lymphoma and sarcoma.
Causes
- Human Papillomavirus infection.
- Chronic use of contraceptives.
- Unprotected sex.
- Early sexual contact and multiple sex partners.
- Compromised immune system
Symptoms
- Abdominal pain
- Heavy menstruation
- Vaginal discharge
- Vaginal dryness
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue
Ways to diagnose
Following are the methods to diagnose cervical cancer:
- Pap test: This is a screening test done for patients who have symptoms of cervical cancer. This is not a confirmatory test. The doctor may advise further diagnosis on the basis of abnormal Pap tests.
- Colposcopy: Colposcopy is done through colposcope which allows the doctor to examine the cervix clearly. Acetic acid can be used to clearly evaluate the abnormal areas.
- Cervical biopsy: Cervical biopsy can be done to conclude the presence of the pre-cancerous and cancerous condition. The tissue is taken from the cervix and seen analyzed to detect any cancerous growth.
- Imaging techniques: Imaging techniques such as MRI, CT and X-ray are used to diagnose the condition.
Risks if neglect
Following are the complications of cervical cancer if the symptoms are neglected;
- Pain: Pain is the major complication of spreading cervical cancer. Pain is caused when the cancer cells invade the nerve endings causing moderate to severe neuropathic pain. Pain may also be caused due to the spread of cancer in muscles and bones.
- Bleeding: Spreading of cancer in the tissues of the vagina, bladder, and rectum may lead to bleeding.
- Respiratory depression: In grade 4, cancer may metastasize to lungs which may lead to respiratory depression.
- Kidney failure: As cancer spreads to the bladder, it may lead to urine build-up inside the urinary system. Especially kidneys. This condition is known as hydronephrosis and has the potential to cause significant damage to kidneys.
- Blood clots: Cervical cancer makes the blood thicker and more viscous. This increases the risk of clotting and thromboembolism which may lead to life-threatening complications.
Stages
There are five grades of cervical cancer. These grades are divided on the basis of the severity and progression of cancer. Five grades are as follows:
- Grade 0 cervical cancer: This is called as a pre-cancerous stage in which abnormal cells are found in the cervix which has the potential to grow into cancerous cells.
- Grade 1 cervical cancer: This is the initial stage of cervical cancer. At this stage, the cancer cells are present only in the neck of the cervix. The stage is further subdivided into 1A and 1B on the basis of the size of the cancerous area.
- Grade 2 cervical cancer: Cancer of this grade has started to spread into the surrounding tissues but not have spread aggressively into the surrounding tissues such as muscles or in the inferior part of the vagina. This grade is further divided into grade 2A and 2B on the basis of the spread of cancer in nearby tissues.
- Grade 3 cervical cancer: This grade is characterized by the spread of cervical cancer into the pelvic region. Cancer has aggressively spread to the surrounding tissues including muscle and ligaments. The cancerous cells have also invaded the whole of the vagina.
- Grade 4 cervical cancer: This grade of cervical cancer is characterized by the metastasis of cancer. This may spread to the nearby organs such as bladder or rectum and may also invade far organs such as lungs.
Foods to eat and avoid
Foods to eat:
- Citrus fruits
- Yogurt
- Spinach
- Tomatoes
- Chicken
- Garlic
- Broccoli
- Cabbage
- Soy
- Apple
- Avocados
- Carrots
- Pink grapefruit
Foods to avoid:
- Potato chips
- Fried and spicy foods
- Foods containing trans fats
- Refined sugar
- Processed Meats
Prevention tips
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle such as exercise and a healthy diet.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol.
- Immediately take advice from the doctor in case of experiencing symptoms.
- Get vaccinated for HPV infection.
- Always use protective measures while doing sex.
- Undergo a routine Pap test and follow-up.
When to see a doctor
Call your doctor if:
- You have heavy menstrual bleeding.
- You have vaginal discharge.
- You feel vaginal dryness.
- You feel abdominal pain and pain during sex.
- You have bowel problems or urinary problems.
- You have any other symptoms that make you more concerned.
Do’s & Don’ts
Do’s
- Limit the consumption of alcohol.
- Always indulge in protected sexual activities.
- Be informed about the symptoms and causes of cervical cancer.
- Follow a healthy lifestyle.
- Take healthy nutrition.
- Do regular exercise.
- Call the doctor in case you have heavy bleeding, vaginal discharge, and vaginal pain during sex.
Don’ts
- Do not ignore any cervical symptom.
- Do not smoke.
- Do not miss the next scheduled date to visit healthcare professional.
- Do not shy to ask further information regarding the disease and your condition.
Risks for specific people
Patients with Human Papillomavirus infection and chlamydia infection are at increased risk of contracting cervical cancer. Smoking and obesity also increase the risk of cervical cancer. Immunocompromised people and women with chronic use of contraceptives also have a relatively higher risk of cervical cancer.