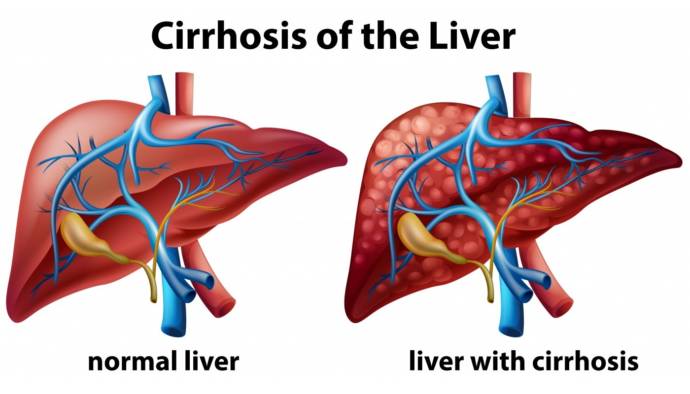
Liver cirrhosis is the disease of the liver characterized by the presence of a lot of fibrous tissue or scarring. Symptoms of the disease include fatigue, swelling, weight loss, loss of appetite and yellow skin and eyes. The diagnosis is done through physical evaluation, imaging techniques, and blood tests.
Types
Liver cirrhosis is an irreversible disease with life-threatening complications. Following are the types of liver cirrhosis:
- Hepatitis-C cirrhosis: This type of cirrhosis is caused due to hepatitis C infection. The hepatitis C patients have chronic inflammation and scarring in their liver leading to cirrhosis. Further, drinking alcohol in the presence of hepatitis C also increases the risk of liver cirrhosis.
- Primary biliary cirrhosis: Primary biliary cirrhosis is said to be an auto-immune disorder. The body eats up its own cells resulting in a lot of scars developing inside the liver. Inflammation develops in the liver leading to the damage of hepatocytes. It also leads to bile duct destruction and the bile duct is replaced with scar tissue. Patient suffering from primary biliary cirrhosis are more prone to certain other medical disorders including osteoporosis and inflammatory arthritis.
- Primary Sclerosis Cholangitis: This condition is caused due to the blockage and destruction of bile ducts. It is a chronic and progressive disease. This is caused by scarring of the bile ducts. As the bile ducts get damaged and scarred, the bile formed in the liver does not leave the liver leading to accumulation of bile in the liver. The bile accumulated in the liver destroys liver cells leading to further complications.
- Alcoholic Cirrhosis: Alcoholic cirrhosis is the condition caused due to excessive intake of alcohol. The liver metabolizes alcohol and excessive alcohol damages the liver cells leading to scarring. The condition becomes more critical when the heavy intake of alcohol is combined with hepatitis C infection.
Causes
Following are the causative factors of cirrhosis:
- Hepatitis C
- Excessive intake of alcohol
- Autoimmune hepatitis
- Medications such as isoniazid
- Fatty liver disease
- Destruction of bile ducts
- Cystic fibrosis
Symptoms
Following are the symptoms occurred in the patients suffering from cirrhosis:
- Weakness and fatigue
- Reduced appetite
- Jaundice
- Weight loss
- Anorexia
- Itchy skin
- Abdominal swelling
- Edema
- Easy bleeding or bruising
- Confusion
- Loss of libido
- Nausea
Ways to diagnose
Following are the methods adopted by the physician for diagnosing cirrhosis:
- Blood test: Blood tests are used to diagnose cirrhosis. The blood test recommended by the physician may include complete blood cells count, liver enzymes, and presence of autoimmune diseases. Blood tests are also performed to test the presence of hepatitis C infection.
- Physical examination: The doctor may perform physical check-up of the body including any swelling in the legs or abdomen or yellowing of the skin and eyes.
- Imaging tests: Various imaging techniques such as MRI, ultrasound and CT scan are performed to diagnose cirrhosis. Further, elastography can also be done to analyze the stiffness of the liver.
- Liver biopsy: In some cases, the physician also recommends a liver biopsy.
Risks if neglect
Following are the complications of unmanaged cirrhosis:
- Splenomegaly: Cirrhosis causes enlargement of the spleen leading to the entrapment of white blood cells and platelets. Cirrhosis may be diagnosed based on low white blood cells in the test report.
- Bleeding: Due to liver damage, portal hypertension occurs leading to pressure in the vessels. This increased pressure may lead to bleeding. Further various coagulation factors are also synthesized in the liver. Damage to the liver tissues hampers the clotting process.
- Infection: Due to cirrhosis, the water or fluid is built up in the abdomen, thereby increasing the risk of infection.
- Hepatic encephalopathy: Liver is the primary organ for performing detoxification inside the body. Any damage or scarring in the liver reduces this function leading to accumulation of toxins in the body and have a destructive effect o the brain cells.
- Malnutrition: Liver metabolizes various nutrients in the body and stores them for immediate need or future need. In cirrhosis, the patient may suffer from malnutrition.
- Portal hypertension: As the tissues of the liver gets damaged and scarring occurs in the liver, there is a reduced blood flow leading to portal hypertension.
Stages
Following are the stages of live cirrhosis:
- Stage I: In this stage, the patient does not experience any symptoms, however, there is an inflammation in the liver.
- Stage II: The functioning of the liver is reduced, and a feeling of fatigue and weakness is experienced by the patient.
- Stage III: Muscle weakness, fluid retention, and depression are experienced by the patient in this stage.
- Stage IV: This stage is characterized by the presence of swelling in the legs and abdomen. Further, the skin and eyes become yellow and the patient suffers from portal hypertension.
Foods to eat and avoid
Foods to eat:
- Beans
- Lentils
- Eggs
- Yogurt
- Milk
- Coffee
- Grapefruit
- Blueberry
- Pears
- Beetroot juice
Foods to avoid:
- Salty foods
- Processed food
- Canned soups
- Undercooked meat
- Raw sprouts
Prevention tips
- Maintain a healthy diet.
- Avoid drinking alcohol.
- Do not involve in unprotected sex.
- Get Hepatitis C vaccination.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Have a screening test for genetic disease if there is a family history of liver disease.
- Reduce your stress.
When to see a doctor
Book an appointment with your doctor if:
- You have constant belly pain.
- You have a feeling of confusion and disorientation.
- You have yellow skin and eyes.
- You have swelling in your legs or abdomen.
- You have breathing problems.
- Any other symptoms that make you uncomfortable.
Do’s & Don’ts
Do’s
- Get vaccination against hepatitis C.
- Take a healthy diet.
- Stay hydrated by drinking enough fluid.
Don’ts
- Do not drink excessive alcohol.
- Avoid unprotected sex.
- Don’t ignore any symptom related to cirrhosis or other diseases.
- Avoid sharing the injection needles.
Risks for specific people
People suffering from hepatitis C infection and who are in the habit of excessive alcohol intake are at significant risk of developing cirrhosis. People with diabetes, obesity and high triglyceride level are also at increased risk of contracting cirrhosis.