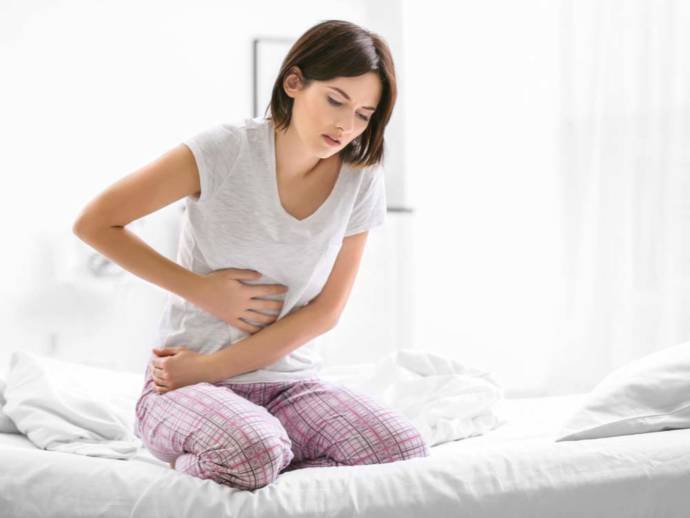
Indigestion, also known as dyspepsia, is the condition that causes gastric discomfort. Indigestion is caused due to peptic ulcer, smoking, drinking alcohol, and overeating. The patient may feel abdominal pain, nausea, and flatulence. Diagnosis can be done through physical evaluation, endoscopy, CT scan or X-ray and lab tests.
Types
Indigestion or dyspepsia is the condition which causes abdominal pain, bloating and benching in the patient. Following are the various types of dyspepsia:
- Organic dyspepsia: Organic diseases are the diseases where there is measurable damage to the tissues or there is an inflammation. These conditions can be diagnosed by evaluating the presence of biomarkers or any biochemical change in the organ, tissue or cell. The causes of organic dyspepsia include peptic ulcer, GERD, gastric cancer, esophageal cancer, other GI or systematic disorder, and intolerance to food or drugs.
- Functional dyspepsia: Functional disease are characterized by the absence of any identifiable or measurable diagnosis. The mechanisms relevant to functional indigestion are ANS-CNS dysregulation, delayed gastric emptying, impaired gastric accommodation, altered sensitivity to fats and lipids, hypersensitivity to gastric distension, and altered gastric electrical rhythm.
Causes
Causes of indigestion or dyspepsia are:
- Peptic ulcer
- Infection
- Delayed gastric emptying
- Gastric distension
- Smoking
- Anxiety and depression
- Overeating
- Medications or underlying diseases
- Fatty and spicy foods
- Carbonated and caffeinated beverages
Symptoms
Patient suffering from indigestion may encounter the following symptoms:
- Abdominal pain
- Flatulence, bloating and belching
- Nausea
- Mild to moderate fever (in the advanced stage)
- Fullness after meal
- Reduced quality of life
Ways to diagnose
Following are the diagnostic methods available for diagnosing indigestion:
- Physical examination: The physician may preliminary diagnose the condition by doing the physical examination on the basis of the symptoms presented by the patient.
- Medical history and food habits: The doctor may ask the medical history of the patient in order to analyze the chance of the underlying disease and also ask about the eating habits. Eating habits are important in evaluating indigestion as they have a significant impact on this condition.
- Endoscopy: In order to evaluate the condition in-situ, the doctor may use endoscopy. This is done to evaluate the tissue damage in the upper gastric tract.
- Imaging techniques: X-ray or CT scan is done to analyze underlying disease or any obstruction that limit the capacity of digestion.
- Blood test: Blood tests and other lab tests can be advised to diagnose reasons for the symptoms presented. It also helps in identify anemia or other medical conditions.
- Breath and stool tests: Breath and stool test is done to test the presence of H. pylori.
Risks if neglect
Although indigestion is mild and can be managed effectively, sometimes severe indigestion may lead to the following complications:
- Pyloric stenosis: Pyloric stenosis is caused due to the continuous irritation of the wall of the stomach lining due to acid. In this condition, the passage between the stomach and the intestine gets narrowed and the food does not able to move freely. This leads to improper digestion. The treatment of this condition is through surgical intervention.
- Peritonitis: Indigestion, if not managed at the initial stage, may lead to the damage of the lining of the intestinal tract. Although, the condition is usually caused due to bacterial or fungal infection, repeated effects of acid on the peritoneum causes peritonitis. Surgical intervention and medications are the options for treating peritonitis.
- Esophageal stricture: In conditions such as GERD, the acid bounce back from the stomach to the esophagus leading to esophageal stricture. If GERD remains for a long period of time, it may damage the esophageal wall and result in the construction of esophagus. Surgery is required to treat the condition.
- Reduction in quality of life: Chronic indigestion severely reduces the quality of life and make the patient uncomfortable. It leads to absence from schools and offices.
Stages
Stages of indigestion are divided on the basis of the severity of the symptoms. Following are the stages of indigestion:
- Stage I or early stage: The symptoms of the early stage indigestion are generally caused by the food itself. The symptoms presented in this stage are bloating, flatulence, distension of the stomach and acidic or oily belching. The other symptoms of this stage are nausea and loss of appetite.
- Stage II or advanced stage: The symptoms of this stage occur due to tissue damage. Inflammation occurs at this stage. The patient may also experience mild to moderate fever.
Foods to eat and avoid
Foods to eat:
- Honey
- Yogurt
- Apple
- Walnuts
- Rice
- Bread
- Fresh orange or grapefruit juice.
- Carrot
- Fenugreek
- Buttermilk
- Aniseed
- Ginger tea
Foods to avoid:
- Carbonated drinks
- Fatty food
- Spicy food
- Cheese
- Pulses
- Potato
- Tomato
- Chocolate
- Onions
- Cabbage
- Processed food
- Artificial sweetener
Prevention tips
- Do not overeat.
- Avoid spicy food.
- Eat slowly with proper chewing.
- Stay away from stress and anxiety.
- Avoid smoking and limit the intake of alcohol.
- Avoid carbonated as well as caffeinated beverages.
- Avoid doing exercise with a full stomach.
- Eat your dinner three hours prior to going to bed.
- Walk for a few minutes after eating food.
When to see a doctor
Book an appointment with your doctor if:
- You have bloating, benching or stomach pain.
- You have heartburn.
- You feel uncomfortable after eating food.
- You have unexplained weight loss.
- You have blood in vomiting.
- You have bloody stools.
- You have severe stomach pain.
- You have shortening of breath.
- You have any other symptoms that concern you.
Do’s & Don’ts
Do’s
- Take a healthy diet.
- Incorporate fresh juices in your diet.
- Take a walk after eating.
- Eat slowly and with proper chewing.
- Use pillow while sleeping.
- Do meditation to remain stress-free.
Don’ts
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not smoke.
- Do not go directly to bed after having dinner.
- Do not eat too spicy food.
- Do not exercise just after eating food
Risks for specific people
Indigestion is generally found in the people who drink alcohol in excess. Patient on certain medication such as aspirin also has increased the risk of this condition. People with emotional stress and suffering from anxiety and depression have an increased incidence of indigestion. People on hormone replacement therapy also develop indigestion.
Home remedies for indigestion
- Apple cider vinegar and honey: 1 teaspoon of Apple cider vinegar and 1 teaspoon of honey are mixed in half to a 3/4th glass of water and drink 15 minutes prior to eating the meal. This will help in reducing indigestion.
- Chamomile tea: Make chamomile tea by putting the teabag in a cup of boiling water. Allow for a few minutes to bring the extract in the solution. Drink the solution by sipping.
- Baking soda solution: Half teaspoon of baking soda is added to a ½ glass of lukewarm water. Drink the solution twice a day.
- Essential oil: 1-2 drops of essential oil such as lemon oil or ginger oil is added to a glass of warm water and consumed. The essential oil has a soothing property that helps reduce indigestion.
- Aloe Vera juice: 2-3 teaspoon of concentrated Aloe Vera juice is mixed in half-a-glass of water and consume it by sipping.
- Fennel extract: Add 1 teaspoon of fennel seed in hot water. Leave it for 10 minutes. Strain the solution. Consume the solution through sipping.
- Ajwain seeds: ½ teaspoon ajwain seeds are mixed with a pinch of rock salt. Eat the mixture along with half a glass of water.
- Massage therapy: Equal quantity of garlic and soy oil are mixed, and the mixture is massaged over the stomach. This will provide relief from stomach pain and indigestion.