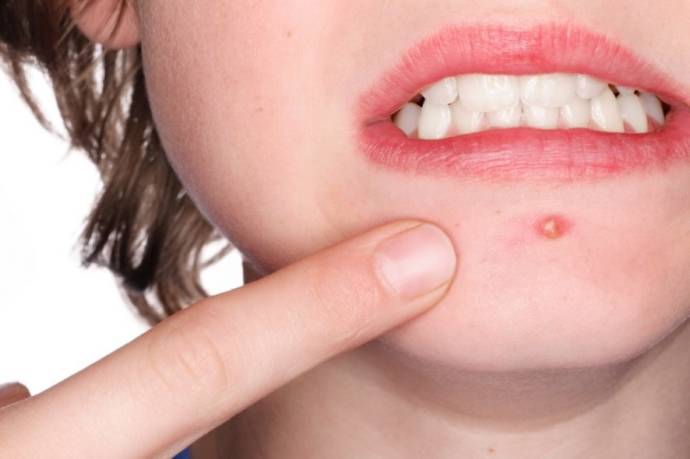
Pustules are the skin eruptions, which are filled with fluid contains oil, cellular debris, and pus. Pustules are caused due to various diseases such as acne, candidiasis, chicken pox and smallpox. The diagnosis of the cause of pustules can be done through blood tests, serological examination, immunological assay, and re-challenge test.
Types
Following are the different types of pustules:
- Acute generalized pustules: This condition is also known as Acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis. This is a rare condition and in most of the cases, caused due to the administration of medications. Thus, this condition is also known as pustular drug eruption or toxic pustuloderma. It occurs within 3-5 days after the administration of an allergic drug and generally resolves 2-3 days after discontinuation of the allergic medication. However, in some cases, the condition becomes severe and the disease may spread to the liver, lungs or kidney. Further, the risk of secondary infection is significantly increased in this condition.
- Acute localized pustules: These types of pustules are more localized as compared to the generalized pustules. The area which is relatively more affected is face, chest, back, feet, and hands. This type of pustules is generally seen in conditions such as acne vulgaris, rosacea, perioral dermatitis, and eosinophilic folliculitis.
- Chronic pustules: The symptoms of this type of pustulosis are chronic. The symptoms of pustular psoriasis are acute, subacute or chronic.
Causes
Following are the causes of pustules:
- Psoriasis
- Chickenpox
- Rosacea
- Candidiasis
- Boils
- Acne
- Cold sores
- Impetigo
- IgA pemphigus
- Smallpox
Symptoms
- Fever and chills
- Fatigue
- Body aches
- Pus-filled eruptions
- Localized redress and warmth
- Eruptions are tender to touch
- Pain
Ways to diagnose
Pustules can be caused due to various conditions and are diagnosed according to the symptoms presented by the patient. Following are the diagnostic criteria for diagnosing the cause of pustules:
- Time of onset and duration: Time of onset and duration are useful in finding the cause of the pustules for example pustules from drugs occurs 3-4 days after drug administration.
- Associated symptoms: Associated symptoms also required to evaluate the pustular condition, such as in secondary syphilis, the patient experiences various other symptoms.
- Medical history: Medical history of the patient also helps in diagnosing the disease. People with psoriasis are at high risk of developing pustular psoriasis.
- Clinical examination: In clinical examination, size of pustules, the location of pustules and its pattern are evaluated. For instance, in pustular folliculitis, the size of pustules is 2-10 mm. Pustules due to impetigo and folliculitis generally occur on traumatized skin. In acne vulgaris, the comedones are seen along with pustules.
On the basis of the above factors, primary identification of the disease is done. Confirmatory diagnosis can be done through the following methods:
- a) Blood test: Blood test is done to identify whether there is any infection. Blood test includes Complete blood cell count, liver function test, serum creatinine level and thyroid stimulating hormone.
- b) Serological testing: For the confirmation of candidiasis as the cause of pustules, serologic 1,3-beta glucan can be done.
- c) Skin biopsy: Skin biopsy is done to determine the exact cause of pustules. Special staining is done to identify if the cause of pustules is an infection.
- d) Re-challenge test: If there is a suspicion that the muscles are caused due to any medications, then re-challenge test or patch testing can be done.
- e) Immunological testing: In the infection suspected with HIV as a cause of pustules, your doctor may recommend DNA analysis through Polymerase Chain Reaction.
Risks if neglect
Following complications may develop if the pustules and its causes are not managed:
- Furunculosis: Unmanaged folliculitis may babe infection deep into the follicles leading to abscess formation and necrosis.
- Permanent hair loss: Folliculitis may lead to permanent hair loss as t results in the complete destruction of follicles.
- Acute respiratory distress: Presence of inflammatory mediators in any form of the pustular disease leads to acute respiratory distress syndrome.
- Septic shock: Pustules are generally caused due to the infection, caused due o bacteria, virus and fungi. The infection in the blood may lead to septic shock. Further, this infection also has the potential to spread in vital organs such as the liver, kidney, and brain, leading to further complications.
Stages
The stages of the pustules are characterized on the basis of the symptoms experienced by the patient. In mild pustule stage, the patient feels only mild symptoms and there is no discomfort felt by the patient. Redness, pain and itching increase as the pustules enters in moderate and severe stages. Pustules due to different diseases have different severity levels.
Foods to eat and avoid
Foods to eat:
- Beetroot
- Carrot
- Sweet potato
- Spinach
- Blueberries
- Walnuts
- Onion
- Corn
Foods to avoid:
- Peanut
- Sugar
- Coffee
- Bread
- Dairy products
- Soy foods
- Spicy food
Home remedies for pustules
There are various causes of pustules and it is important to treat the underlying cause. Generally, the most common cause of pustules is acne vulgaris. Following are the general home remedies that can help in the management of pustules:
- Calamine lotion: Calamine lotion is used to dry up the pustules and reduce inflammation. It will also help in reducing the scarring.
- Cleansers: Mild cleansers are used to remove the dirt and oil from the clogged pores.
- Ice packs: Cold packs are applied on the pustules to reduce inflammation. Ice is kept in the Ziploc bags and applied on the pustules for 5-10 minutes. Do not apply for a longer period as it may damage the skin.
- Warm compress: Warm compress can be used on the pustules to drain them. The cloth is soaked in hot water and slightly pressed on the pustules to drain the fluid filled inside the pustules. It is far better than squeezing due to its low risk of infection.
- Face steaming: The primary target for managing the pustules caused due to acne is maintaining the proper facial cleanliness. Facial steaming is a fantastic procedure for removing the oil and dirt from the clogged pores.
- Essential oil: Essential oils such as lavender oil and tea tree oil are excellent when it comes to managing pustules. These oils are effective antibacterial agents and eradicates bacteria, which are primary cause of pustules. Lavender oils help in reducing inflammation caused due to pustules.
- Herbal remedies: Evening primrose oil can be used topically to get rid of pustules due to acne. Oats face mask can be applied on the pimples to reduce the severity of the condition. Oat face mask can be prepared by mixing oatmeal, honey and eggs. Fresh crushed onion can be applied on skin to reduce bacterial infection. Papaya juice and strawberry juice can also be applied to manage the condition.
Prevention tips
- Wash your face to remove dirt with a moisturizing face wash.
- Cover your face while going out in bright sunlight.
- Gets vaccinated for the disease-causing pustules.
- Take a healthy diet.
When to see a doctor
Book an appointment with your healthcare provider if:
- If you feel severe pain in pustules.
- If your symptoms do not subside or worsen even after taking prescribed medications.
- If the fluid is leaking from the pustules.
- If you have a sudden flare of pustules.
- If you are experiencing fever along with pustules.
Do’s & Don’ts
Do’s
- Do wash your face.
- Maintain proper hygiene.
- Incorporate antioxidant into your diet.
- Take medications as prescribed.
- Avoid smoking and alcohol drinking.
Don’ts
- Do not rupture the pustules.
- Do not do shaving if you have pustules as it may cause infection.
- Avoid exfoliating your skin.
- Do not self-medicate and take advise from the doctor if you have skin abnormality.
Risks for specific people
People with stress and oily skin are more prone to developing acne pustules. People with the autoimmune disease are at significant risk of contracting pustular psoriasis. Children with poor hygiene are at risk of developing infections which result in pustules.