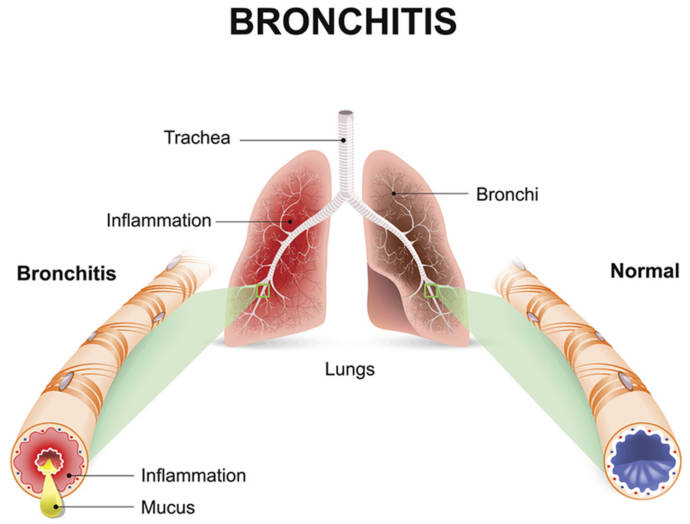
Bronchitis is the inflammation of the lining of bronchioles. The lining gets irritated and inflamed due to infection, pollution or smoking leading to secretion of mucus. Increased mucus secretion causes chest congestion, discomfort, difficulty breathing and fever. Bronchitis can be acute and chronic.
Types
On the basis of the period of symptoms, bronchitis is divided into the following two types:
- Acute bronchitis: This is an acute form of bronchial inflammation with the symptoms persisting for three weeks. Symptoms in some people may remain for six weeks. A cough is the most common symptoms for acute bronchitis. Other symptoms include chest discomfort, fever and difficulty breathing. Viral infection is the most common cause of this form of bronchitis. This is generally found in people who have exposure to pollution and dust. In some cases, it may also be caused due to bacterial infection. This type of bronchitis is found mostly in winter.
- Chronic bronchitis: Chronic bronchitis is the condition characterized by the presence of chronic cough for at least 3 months for two or more consecutive years. Chronic bronchitis is diagnosed through exclusionary methods in which other reasons of a cough are excluded. It is caused due to the consent inflammation in the lining of the bronchial wall. Chronic bronchitis is often accompanied by another condition known as Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder. The common cause of chronic bronchitis is smoking and continuous inhalation of hazardous substances.
Causes
- Infection: Infection is said to be the most common cause of acute bronchitis. Bronchitis can be caused due to viral, fungal and bacterial infection, and viral infection has a high rate of causing bronchitis.
- Pollution: Bronchitis is also caused due to pollution. Bronchitis is the condition of inflamed bronchioles. The inflammation is due to irritation which is developed due to the particles present in the air. This inflammation leads to the production of mucus.
- Smoking: People with the habit of smoking are highly prone to develop bronchitis. This is due to the fact that various chemicals present in cigarette irritate and inflame the bronchial lining.
- Occupational inhalation: Some cases of chronic bronchitis are caused due to inhalation of concentrated chemicals while working in such environment. The incidence of bronchitis can be reduced by wearing safety masks.
- Poor immunity: People with the compromised immune system are significantly at greater risk of contracting bronchitis as their bronchial gets inflamed even with a mild infection.
- Poor Hygiene: People with poor hygiene are also susceptible to developing bronchitis. Further, bronchitis is a contagious disease thus people suffering from bronchitis should follow a hygiene lifestyle to protect other people from contracting the disease.
Symptoms
Following are symptoms presented by the people suffering from bronchitis:
- A cough
- Chest congestion
- A runny nose
- Difficulty breathing
- Chest discomfort
- Chills or fever
- Mucus secretion
- Fatigue and tiredness
- A sore throat
- Cardiovascular complications such as ankle swelling
How to diagnose
Various diagnostic procedures are available to diagnose bronchitis:
- Spirometry: Spirometry is the test performed to assess the capacity of the lungs. This helps the physician to find out how much air your lungs can hold in a single breathing process. This test is done when you complain about breathing difficulties. Spirometry also allows the physician to identify other breathing disorders.
- Sputum test: Sputum test is indicated in the condition when the patient has an uncontrolled and continuous cough. The test is done to identify the cause of mucus secretion.
- Imaging techniques: Imaging techniques such as chest X-ray or chest MRI is done to diagnose bronchitis and also exclude the presence of other serious medical condition.
- Lab tests: Various lab tests including pulse oximetry, complete blood count and material blood test evaluation are counted to analyze the functional capacity of the lungs.
Risk neglecting Bbronchitis
If the bronchitis is not treated, it may lead to the following complications:
- Pneumothorax: Untreated bronchitis may lead to pneumothorax. It is the condition caused when the air from the lung leaks into the space between the lungs and chest wall. The air pushes the lungs from outside leading to lung collapse.
- Pneumonia: If the bronchitis is not treated, it may lead to pneumonia. Bronchitis due to bacterial infection is more likely to progress in pneumonia then bronchitis caused by viral infection.
- Cardiovascular complications: As the body has difficulty breathing, this will put extra stress on the heart, leading to cardiovascular complications.
- Respiratory depression: Bronchitis cause difficulty breathing. When the condition of bronchitis is not managed, severe chest congestion occurs. This may cause respiratory depression.
- COPD: Untreated bronchitis may progress into Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder. As the condition of bronchitis progresses, the alveoli sacs become less flexible leading to difficulty breathing. This condition is known as COPD.
- Aspiration pneumonia: Aspiration pneumonia is also a complication of neglected bronchitis. It is caused when the food or liquid is inhaled into the lungs.
Stages
The stages of chronic bronchitis are determined on the basis of the severity of the disease. The severity of disease is determined by the GOLD system. The GOLD system takes into consideration various factors such as severity of symptoms, the capacity of the lugs, the progression of the disease and other related health conditions. Following are the stages of chronic bronchitis:
- Mild: When FEV1 is around 80%.
- Moderate: When FEV1 is in between 50% to 80%.
- Severe: When FEV1 is in between 30% to 50%.
- Very severe: When FEV1 is below 30%.
Foods
- Ginger
- Black pepper
- Turmeric
- Tomato soup
- Hot water
- Probiotics
- Leafy green vegetables
- Garlic
- Citrus fruits
- Fermented foods
Prevention tips
- Maintain proper hygiene such as washing hands.
- stay away from pollution or irritating inhalants.
- Avoid smoking.
- Stay away from people having bronchitis.
- Take a healthy diet to improve immunity.
When to see a doctor
Visit your doctor if:
- You have a severe cough that lasts for long period.
- You have blood mixed sputum.
- You feel fatigue and have a fever.
- You experience difficulty in breathing.