Diabetes patients need to keep blood sugar levels within the safe range to avoid long-term complications. People with type 1 diabetes cannot produce enough insulin to use blood glucose. Again, patients with type 2 diabetes develop insulin resistance making it difficult to process blood sugar.
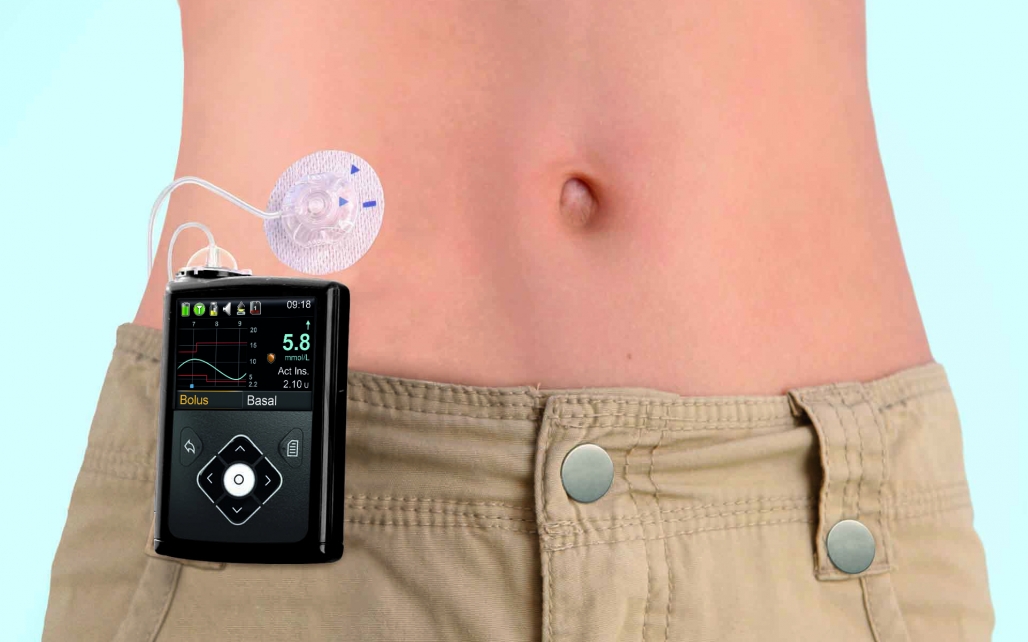
These patients require insulin therapy to make up for insulin deficiency. They can either inject insulin supplements using a needle or use an insulin pump which is a small computerized device to administer insulin. The insulin pump directly delivers the hormone under your skin through a thin tube.
How Does an Insulin Pump Work?
The insulin pump releases a steady flow of the hormone called basal insulin throughout the day as well as during the night to maintain normal levels of insulin. An extra dose of insulin released at mealtime is called a bolus. It is administered to handle rising levels of blood sugar obtained from the food.
You can program the pump to release the basal and bolus doses. You can also program the pump to release a large bolus dose to cover the carbs when you overeat. The insulin pump is not more than the size of a smartphone.
You need to attach the pump to your body with the aid of an infusion set containing a thin plastic tubing and a needle or a cannula. The cannula is a small tapered tube that you place under your skin.
A standard procedure is to place the cannula under the skin of your belly, thigh, or buttocks. This place is called the infusion site.
Certain insulin pumps also include an inserter to easily place the cannula in hard-to-reach areas. Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver small but continuous doses of insulin to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
Insulin Pump Advantages
Insulin pumps have various advantages over syringes. These include:
- You do not require more needle sticks.
- You receive more accurate shots and therefore better management of blood sugar levels.
- Your blood sugar will rarely go low even if you have hypoglycemia.
- A periodic dose of insulin through the pump improves your A1c levels.
- You can easily manage the dose for meals and snacks.
- You can easily follow an exercise regimen.
- You can effectively manage the dawn phenomenon, the unusual sugar spikes early morning.
The pumps work great but it is advisable to keep regular injectable insulin handy just in case the insulin pump stops working.
These patients require insulin therapy to make up for insulin deficiency. They can either inject insulin supplements using a needle or use an insulin pump which is a small computerized device to administer insulin. The insulin pump directly delivers the hormone under your skin through a thin tube.
How Does an Insulin Pump Work?
The insulin pump releases a steady flow of the hormone called basal insulin throughout the day as well as during the night to maintain normal levels of insulin. An extra dose of insulin released at mealtime is called a bolus. It is administered to handle rising levels of blood sugar obtained from the food.
You can program the pump to release the basal and bolus doses. You can also program the pump to release a large bolus dose to cover the carbs when you overeat. The insulin pump is not more than the size of a smartphone.
You need to attach the pump to your body with the aid of an infusion set containing a thin plastic tubing and a needle or a cannula. The cannula is a small tapered tube that you place under your skin.
A standard procedure is to place the cannula under the skin of your belly, thigh, or buttocks. This place is called the infusion site. Certain insulin pumps also include an inserter to easily place the cannula in hard-to-reach areas. Insulin pumps are programmed to deliver small but continuous doses of insulin to maintain optimal blood sugar levels.
Insulin Pump Advantages
Insulin pumps have various advantages over syringes. These include:
- You do not require more needle sticks.
- You receive more accurate shots and therefore better management of blood sugar levels.
- Your blood sugar will rarely go low even if you have hypoglycemia.
- A periodic dose of insulin through the pump improves your A1c levels.
- You can easily manage the dose for meals and snacks.
- You can easily follow an exercise regimen.
- You can effectively manage the dawn phenomenon, the unusual sugar spikes early morning.
The pumps work great but it is advisable to keep regular injectable insulin handy just in case the insulin pump stops working.
Insulin Pump Disadvantages
The following are some of the disadvantages of insulin pumps:
- You are required to enter and update the information for the insulin pumps all day.
- You need to change the infusion set after a few days.
- You need to be careful while using an insulin pump.
- You should periodically check your blood sugar to analyze if the pump is working right. In the case of disfunction or overdose, you risk getting diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which is a life-threatening condition.
- You may require a little hands-on training before you start using the pump. This implies several visits to your health care provider or hours of outpatient training.
- Supplies for the pump can be expensive.
Whether to use the pump or not depends on various factors. You should not opt for an insulin pump if:
- You do not want people to know you are diabetic.
- Wearing a device makes you feel uncomfortable.
- You find the pump difficult to operate.
- You do not want to keep checking your blood sugar over and over again throughout the day.
- You are confused about insulin dosing, physical activity, and carbs.
You must consider some factors before you decide to use one. Insulin pumps are available in a wide variety such as traditional pumps, tubeless pumps, or pumps with a handheld remote.
You must pick one that collaborates with your lifestyle choices. Pump reservoirs can hold insulin doses as low as 176 units to as high as 315 units. Certain insulin pumps can deliver small amounts for kids and people with insulin sensitivity.
Others have features like carb counts for common foods, continuous glucose meter (CGM), and interactivity with phone or laptop.
Insulin pumps are covered by most insurance companies. You can also seek financial aid from pharmaceutical companies if you cannot afford medical supplies.
Concerns about insulin pumps
- You are required to enter and update the information for the insulin pumps all day.
- You need to change the infusion set after a few days.
- You need to be careful while using an insulin pump.
- You should periodically check your blood sugar to analyze if the pump is working right. In the case of disfunction or overdose, you risk getting diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which is a life-threatening condition.
- You may require a little hands-on training before you start using the pump. This implies several visits to your health care provider or hours of outpatient training.
- Supplies for the pump can be expensive.
Factors you Need consider before you buy Insulin Pump
Whether to use the pump or not depends on various factors. You should not opt for an insulin pump if:
- You do not want people to know you are diabetic.
- Wearing a device makes you feel uncomfortable.
- You find the pump difficult to operate.
- You do not want to keep checking your blood sugar over and over again throughout the day.
- You are confused about insulin dosing, physical activity, and carbs.
You must consider some factors before you decide to use one. Insulin pumps are available in a wide variety such as traditional pumps, tubeless pumps, or pumps with a handheld remote.
You must pick one that collaborates with your lifestyle choices. Pump reservoirs can hold insulin doses as low as 176 units to as high as 315 units. Certain insulin pumps can deliver small amounts for kids and people with insulin sensitivity.
Others have features like carb counts for common foods, continuous glucose meter (CGM), and interactivity with phone or laptop.
Insulin pumps are covered by most insurance companies. You can also seek financial aid from pharmaceutical companies if you cannot afford medical supplies.