According to statistics, the male factor of infertility is observed in 40-50% of all cases. The most common cause of pathology is low sperm activity in the ejaculate.
According to statistics, the male factor of infertility is observed in 40-50% of all cases. The most common cause of pathology is low sperm activity in the ejaculate. Because of this, conception by natural means is impossible.
Even carrying out fertilization in artificial conditions do not always allow obtaining a viable embryo. In these cases, you can resort to a special assisted reproductive technology – ICSI procedures.
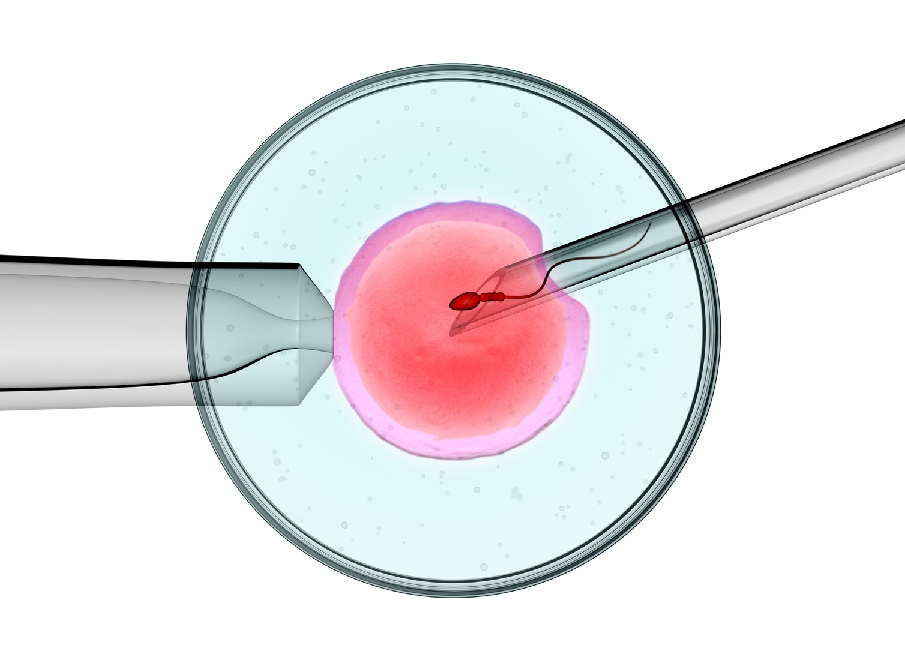
The ICSI procedures, or intracytoplasmic sperm injection, allow for the artificial introduction of a sperm cell directly into an egg cell. This is an additional IVF protocol.
Based on this approach, a mature egg and sperm are combined through a more complicated scheme. An embryologist performs the following steps:
- Selects high-grade mature oocytes and active morphologically high-grade spermatozoa. Spermatozoa can be isolated from sperm. In this case, it is enough to detect even one viable sperm cell and place it in a micro-needle tool (the inner diameter of this needle is slightly larger than the diameter of the sperm head — 6 microns).
- Gets the spermatozoids selected for ICSI procedures immobilized: their tails are compressed so that after their introduction into the oocytes, they couldn’t get out.
- Places the egg in a certain way, fixing it with the help of negative pressure in a suction cup so that the oocyte couldn’t move during the ICSI procedure.
- Inserts the most viable sperm into the cytoplasm of the egg, injecting the sperm with a needle under the control of a microscope.
- Releases the negative pressure in the suction cup along with the egg.
- Places the fertilized egg into an incubator at a temperature of 37 ° C and a carbon dioxide concentration of 5%.
ICSI is currently used in about half of IVF cases. This procedure can lead to a successful conception, even if only one healthy spermatozoon is found in the ejaculate.
However, there are some contraindications to ICSI:
- severe somatic pathology;
- severe mental health disorders;
- HIV infection;
- malignant neoplasms of any localization;
- malformations of the uterus, making it impossible to bear a fetus;
- hematologic malignancies;
- severe anemia;
- submucosal uterine fibroids with deformation of the uterus, of a significant size or with the presence of multiple nodes;
- severe diabetes;
- severe diseases of the nervous system;
- diseases of the heart and blood vessels;
- adenomyosis.
In all the cases, a doctor decides on the possibility of ICSI. Conducting IVF with ICSI made it possible to experience the joy of having a child even to those who had failed in performing classical IVF.
Source: https://ivf-international.com