Artificial pancreas is an FDA approved device that helps diabetics to automatically control their blood sugar levels. It works just like the human pancreas and is designed to release insulin in response of the blood sugar levels that keep changing.
Basically, it is a hands-free, continuous device through which glycemic control can be done using a digital communication technique and advanced algorithms. They work as a treatment especially for the Type 1 diabetes.
Need of artificial pancreas
When patients are using insulin pumps, they need to test their blood sugar levels periodically and regularly. Artificial Pancreas helps to give better readings and also lowers down the burden on the patients as the insulin pump and the blood glucose monitoring device works together.
Downfall of artificial pancreas
There are many advantages of Artificial Pancreas but along with that there are several disadvantages. It does take away a huge burden from diabetic patients.
The glucose monitor that measures the glucose level does not change as quickly as the levels in the blood which can lead to inappropriate dosage of insulin when the levels of glucose are very high or low.
Moreover the systems are not completely automated but up to a certain extent it also requires the involvement of patients. The devices are not invasive compared to the needles so there are chances of formation of scar tissues around the places where there are implants.
These devices are costly and the price varies depending on the provider and the scheme you opt for.
Faster, better and smarter insulin have been developed
There are several challenges but one of the biggest one in creating them is that currently insulin fails to react quickly to big changes in the blood glucose levels. That is why the insulin is usually given before the meal so when the patient has his meal, it is able to react properly.
To overcome this challenge, Novo Nordisk launched Fiasp which is the first new generation insulin. It is much faster than the conventional insulin.
Most of the insulin takes 10-15 minutes to start acting but Fiasp starts acting after a couple of minutes. But still much improvement is needed in the reaction time to the changing blood glucose.
Another challenge is to make more concentrated formulas which can make the devices much smaller in size.
But this is a tough thing because if you increase the insulin concentration then the insulin is absorbed much slower. But Aercor has been able to achieve success up to a great extent on this one.
How they work
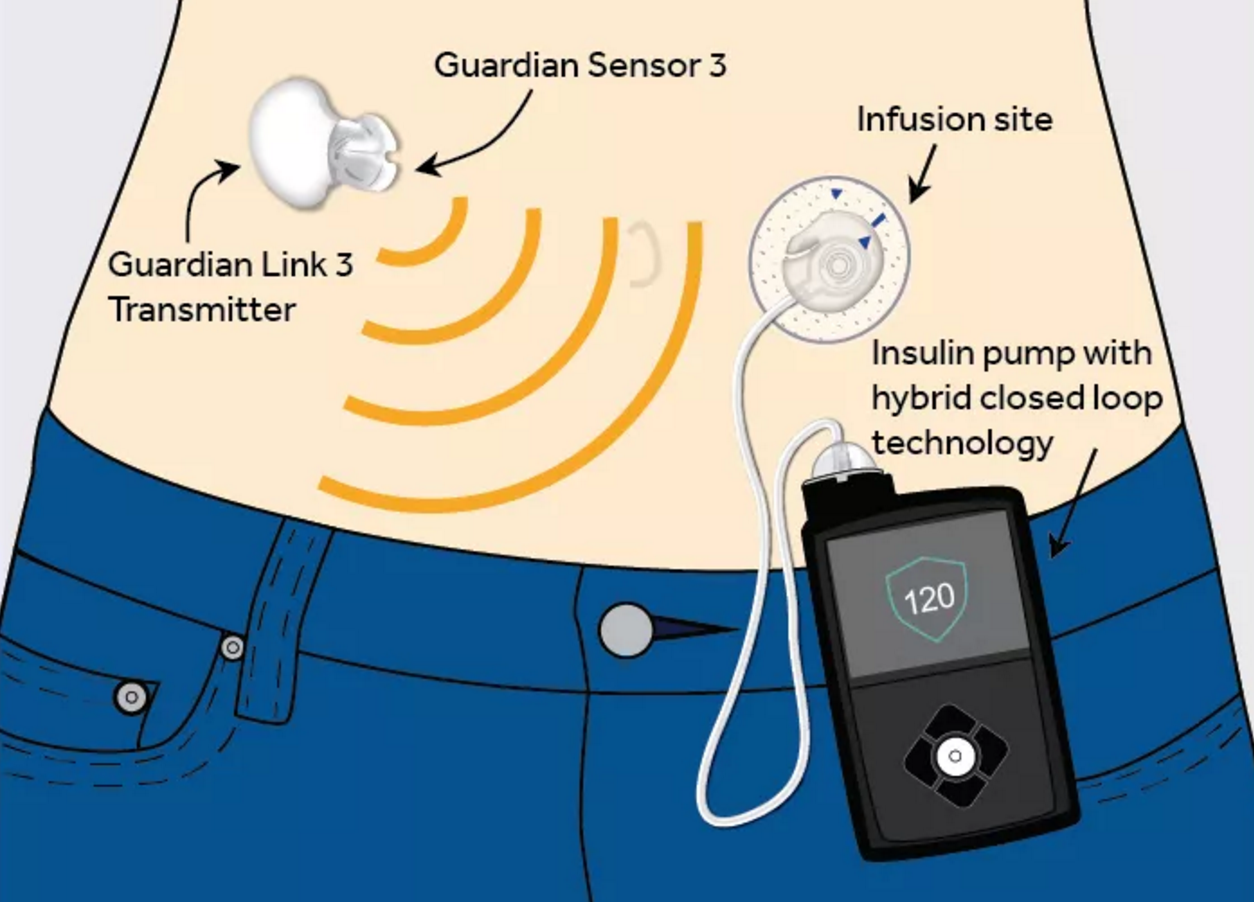
The device has a sensor, continuous glucose monitor (CGM) and an insulin infusion pump. The sensor is worn under your skin and the continuous glucose monitor and insulin pump is worn on your body underneath your clothes. The CGM and insulin pump work hand in hand and respond to the changing blood sugar levels.
At an interval of every 5 minutes, The CGM uses the sensor to check the level of blood glucose. It sends the reading to the insulin pump. When the level is too high, the insulin infusion pump automatically pumps a measured quantity of insulin into the body through the patch and a catheter.
When the levels reach the normal range, it stops. It is compatible with a smartphone app which enables you and your doctor to keep a track of blood sugar levels and doses.
Artificial Pancreas provides approximately two and a half extra hours of blood sugar levels in a day. They reduce the time spent in high and low blood sugar levels and are effective as well as a safe treatment for people having Type 1 diabetes.
Compared to other instruments, researchers found that the artificial pancreas reduced time in hyperglycemia by almost two hours and in hypoglycaemia by 20 minutes.
There are three main types of artificial pancreas system that the researchers are working on:
- Closed – Loop artificial pancreas
- Bionic pancreas
- Implanted artificial pancreas
Closed – Loop artificial pancreas
This is the most widely tested artificial pancreas system also known as ‘closed loop insulin delivery system’.
They combine three functions: the monitoring function performed by CGM, Insulin delivery system which is the pump and a digital controller. Integrating these functions together forms a closed – loop system.
Cambridge University has done extensive research in closed – loop artificial system and their devices are being tested on humans in the home environment and in a controlled manner.
This has a basic mechanism that includes an insulin pump worn on the body which wirelessly communicates with the CGM that is worn on the skin as a patch.
It measures the blood glucose levels and enters it in the computer which calculates the dose of insulin that needs to be delivered into the body by the insulin pump. This does it pumped into the body.
Bionic pancreas
In 2015, bionic pancreas was introduced to help people with Type 1 diabetes to control their blood sugar levels with the help of a device.
Dr. Edward Damiano’s Beta Bionics Firm developed a bionic pancreas that automatically controls the blood glucose levels using two insulin pumps which delivers insulin and glucagon respectively in the body.
The pumps are connected with an iPhone app through Bluetooth which enables them to communicate with each other and calculate the dosage required by the body. At an interval of every 5 minutes, dosage of insulin and glucagon is calculated from the readings.
Implanted artificial pancreas
The Implanted artificial pancreas is a device implanted on the body. Instead of taking two to four injections into the skin at certain intervals in a day, this is an automatic and continuous supply of insulin based on the changing blood glucose levels in the body.
There is a gel that responds to the changing levels of blood glucose in the bloodstream of the body. Once it reaches the normal range the gel re-solidifies which controls the release of insulin.
When the blood glucose levels are high, the gel softens and releases higher rate of insulin in the body and when the levels are low, the insulin released by the gel is less compared to the times when the blood glucose levels were high. This implanted system can regularly be refilled with insulin.