Dehydration is a condition associated with excessive loss of body water. It occurs when the amount of water loss from the body exceeds the intake of water. Our body is composed of 75 percent of water which is essential to maintain our daily activities like metabolism, respiration, urination etc.
Type of dehydration
- Mild dehydration: 3 to 4 percent decrease in total body water is tolerable by most of the people without any adverse effects on body.
- Moderate dehydration: 5 to 8 percent decrease in total body water can cause dizziness and fatigue.
- Severe dehydration: More than 10% decrease in total body water leads to severe decline in physical and mental well being.
- 15% to 20% decrease in total body water may lead to collapse or death.
Causes of dehydration
The primary cause of dehydration is not drinking the sufficient amount of water required by our body. And it happens sometimes because of our busy schedules or lack of facility or availability of portable drinking water (for example during mountain climbing, camping, in villages etc.)
Some other factors which play a supporting role in causing dehydration are as follows:
- Diarrhea: Here body expels large amount of water and hence leads to dehydration. This is the main reason of deaths due to dehydration in infants and children.
- Vomiting: Vomiting is also a well known reason of dehydration. And in case of repeated episodes of vomiting it even become difficult to replenish this loss orally as person sometimes develop an aversion to drink.
- Perspiration: Sweating is basically our body’s own cooling mechanism which leads to evaporation of a particular amount of water. Perspiration is a normal process but it may lead to dehydration under few circumstances, like strenuous physical activity, hot and humid weather and also during fever there is increase in sweating.
- Frequent Urination: There are certain medications which cause increase in frequency of urination such as antipsychotics, antihistamines, diuretics or medicine for blood pressure. Overuse of alcohol may also lead to this condition.
- Diabetes: uncontrolled sugar levels in blood causes frequent urination as well as loss of fluid.
- Heatstroke: Being in the sun for too long can also causes dehydration.
- Reduced water intake: drinking less water during humid and hot climate also produces the signs of dehydration.
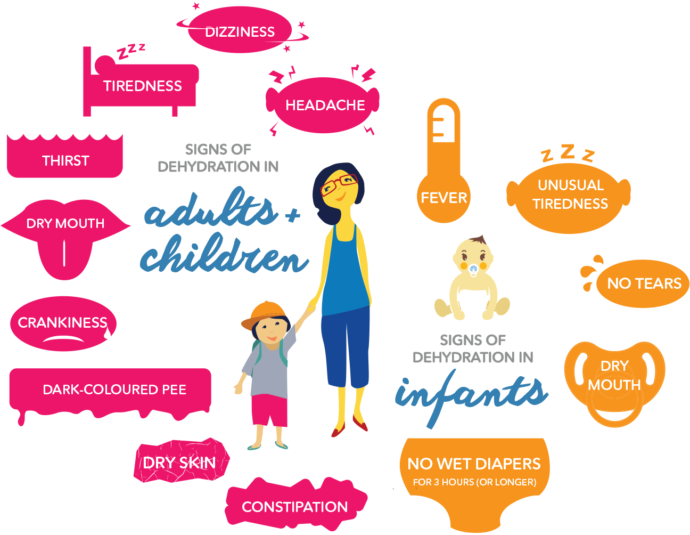
Symptoms of dehydration
It is important to note that symptoms of dehydration differ in every stage. Also they vary in children as well as adults.
- Symptoms of mild dehydration: These are the early signs of dehydration.
- Thirst
- Dark and concentrated urine
- Decrease urination
- Symptoms of moderate dehydration: These symptoms are not fatal and are easily reversible if person start drinking water immediately. These include:
- Dry mouth
- Weakness
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Symptoms of severe dehydration: Symptoms of severe form of dehydration are fatal and may produce serious health hazards. These symptoms are not self limiting and immediate medical supervision is mandatory. These are as below:
- Sunken eyes
- Dry and shriveled skin
- Lack of sweating
- Increased heart rate
- Low blood pressure
- Weak and rapid pulse
- Fever
- Confusion
- Unconsciousness
- Symptoms of dehydration in children below 5 years:

- Crying without tears
- Sunken eyes
- Sunken fontanelle
- Dry mouth with dryness of tongue
- Irritability
- No urination for 3 to 4 hours
- Listlessness
- Shriveled looking hands and feet
How to diagnose
Dehydration can also be diagnosed on the basis of physical signs and symptoms. The color of urine is the best indicator to check the hydration level of a person. Where clear urine indicates a good hydration level, dark color of urine is considered as the sign of dehydration.
To confirm the diagnosis of dehydration in infant, a doctor may look for a soft and sunken spot on the scalp accompanying with loss of sweat and urination.
To confirm the degree of dehydration, your doctor may perform below tests:
- Blood Tests: Blood test is done to check the level of electrolytes present in body, mainly the level of sodium and potassium. These are the basic chemical structures which maintain hydration in our body.
- Urinalysis: It is done to confirm the presence of ketones in urine which also plays a vital role in confirming the diagnosis of dehydration.
Risks if neglected
Dehydration if not treated on time can lead to further complications, which include:
- Heatstroke: This happens when adequate intake of water is not taken during vigorous physical activity under heat of sun with heavy perspiration. This varies in severity from cramps and exhaustion to fatal and life threatening consequences.
- Urinary and kidney problems: Repeated attacks of dehydration may cause urinary tract infection and if it remains prolonged for more time, it may lead to kidney stone and sometimes acute renal failure.
- Seizures: Dehydration causes imbalance of our body’s electrolytic system especially affecting the levels of sodium, potassium and chloride. Reduction in level of these electrolytes can produce involuntary contractions of muscles also called seizures. This is sometimes followed by unconsciousness.
- Hypovolemic shock: It is also known as low blood volume shock. This is the most fatal complication of untreated dehydration which may lead to death. This happens because dehydration causes reduction in body’s blood volume due to which there is a significant drop in blood pressure followed by reduction in oxygen level of the body.
Foods to take and avoid
Drinking 2 to 3 liters of water is advisable to remain well hydrated. Along with this there are many foods that are rich in water content and help in preventing dehydration.
Foods to eat:
- Watermelon – It is made up of 92% water and is the most hydrating food.
- Strawberries
- Peaches
- Oranges
- Tomatoes
- Cucumber
- Zucchini
- Lettuce
- Cauliflower and cabbage
- Coconut water
- Soups
- Broths
- Celery
- Yogurt
Foods to avoid:
- Carbonated drinks
- Coffee
- Energy drinks
- Alcohol
- High protein meals
- Beetroots
- Asparagus
- Artichokes
- Soy sauce
- Fried food
- Non vegetarian food
- Salty and frozen meals
Prevention Tips
The best way to treat dehydration is prevention, which we can easily do by following few simple measures. These are:
- Stay hydrated. Drink plenty of liquids.
- Consume food that is rich in water content – mainly fruits and vegetables.
- Take plenty of water or fluids at regular interval during strenuous physical exercise.
- Drink good amount of water or fluids during hot and humid climate to maintain your body’s normal temperature.
- In case of diarrhea and vomiting, start taking enough water along with oral rehydration solutions as early as possible.
- Elderly people are more prone to become dehydrated during acute minor illnesses, such as urinary bladder infection, lung infection or might be a simple form of influenza. So whatever may be the disease is, make a very good practice of drinking more water if you are feeling unwell.
When to see a doctor
Though dehydration can easily be treated without any medical supervision if noticed earlier and intake of fluids and water is introduced from the earliest sign of dehydration. But being in a state of dehydration for a prolonged period can be life threatening. So immediately call your doctor if you see below symptoms in a patient:
- Diarrhea – If present for more than 1 day
- Stools are black or bloody in color
- Patient is drowsy and inactive
- Disorientation and confusion is there
- A rapid or weak pulse
- Fast respiration
Do’s & Don’ts
Do’s:
- Drink a lot of water and fluids
- Increase the frequency of breastfeeding or formula milk to infants
- Plan your outdoor physical strenuous activities based on the climatic conditions
- Wear loose and comfortable clothes during hot weather
- Oral rehydration solution is the most important thing to start at an early sign of dehydration
- Eat a balanced diet
- Drink after every 15 to 30 minutes during exercise
- Keep drinking water in short intervals after finishing the exercise as well
Don’ts:
- Don’t wait for the thirst. Just keep drinking water throughout the day
- Don’t miss your meal. Maximum of fluids you get from regular meals.
- Don’t exert yourself after encountering any sign of dehydration
- Don’t over hydrate yourself
Risks of specific people
Though a person can become a victim of dehydration at any age. But still few age groups and certain people are more liable to produce dehydration. These are as follows:

- Infants and children: Young children are more prone to develop signs and symptoms of dehydration as they are more susceptible to have diarrhea and vomiting which are the two main causes of dehydration.
- Elderly adults: With increasing age the fluid reserve of body gets reduced and even the acute sense of thirst get greatly diminished.
- People suffering from diabetes: High level of blood sugar makes you more prone to suffer from dehydration. As prolonged medication of diabetes leads to frequent urination.
- People with kidney diseases: Diseases of kidney also alter the formation of urine.
- People with chronic illnesses: Like cystic fibrosis, adrenal gland disorders etc.
- People who workoutside: being in the sun for a more time during hot weather increases the risk of sunstroke, and hence dehydration.
- Athletes: They are more prone to get dehydrated because of their increased physical activity and most of the sports are being played outdoors. For example; marathons, cycling tournaments etc.
- People living at higher altitudes.