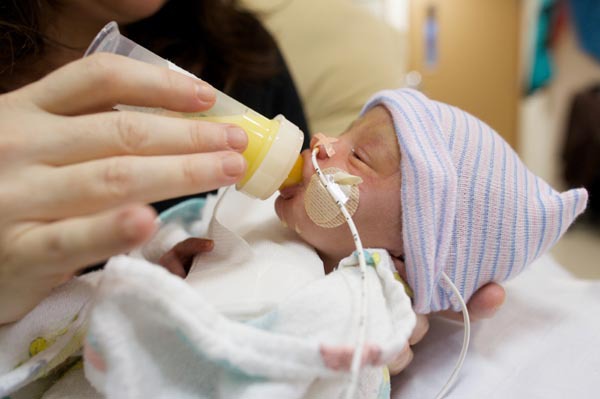
Premature or preterm babies who arrive early, do not get as much time to develop inside the mother’s womb. As a result of this their bodies are not completely equipped to deal with the outside world. They have low birth weight and often face multiple health complications. This is especially true for the babies that are born much before 37 weeks. They need special care and attention to grow up healthy and strong.
Premature babies lose body heat very quickly and so they need some extra energy and care to remain warm. You must be very worried about your child’s health if you’ve given birth to a premature baby and it may help you to learn about some of the early challenges that a premature baby might face. Remember that each baby deals with the challenges in their own way.
But, it will be easier for you to take precautions if you’re armed with more information about the conditions your baby will likely face in the days following its birth. You can rest assured that all doctors and medical specialists have a lot of experience in helping premature babies with their early challenges. After coming back from the hospital, such a baby will need regular nursing by a trained nurse. Mothers will also need to put in extra effort while carrying and nursing for their little one.
Read on to find out more about the most common health problems that preterm babies suffer from.
Breathing Problems
Breathing problems are very common and they are seen in one out of every ten premature newborns. This happens because their lungs are small and immature and they are born with a soft ribcage and weak breathing muscles. If this goes untreated, the lack of oxygen can damage other organs like the brain, eyes or ears. Doctors often artificially introduce a substance called surfactant in the lungs that makes breathing easier. Some of the common lung problems that a premature baby may face are-
- Respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) when the lungs can’t absorb enough oxygen and may need a breathing machine.
- Apnoea of prematurity when the baby has irregular breathing.
- Chronic lung disease (CLD) when the baby needs oxygen for more than 28 days.
Heart & Blood Problems
According to many pediatricians, premature babies have a tendency to develop heart problems in their early days. The most common challenge they might face is called patent ductus arteriosus or PDA. This happens when blood vessels that were supposed to get closed after birth, remain open. This overloads the blood circulation between the heart and lungs and Doctors will recommend necessary medication to close the blood vessel and if this doesn’t work, the baby may need surgery.
Premature babies have been often found to bleed easily. These happens as a result of low platelet count or because the baby has delicate blood vessels. Anemia is another common condition that may be seen in a premature baby and this needs to be treated through blood transfusions.
Damage to the Brain
Premature babies are at a risk of bleeding in the brain soon after birth. This is called intraventricular hemorrhage which happens due to tear in delicate blood vessels or high or low blood pressure. Bleeding in the brain or hypoxia (lack of oxygen) can lead to cerebral palsy, learning difficulties, speech problems, dyspraxia or clumsiness etc.
Eye Conditions
The eyes of a premature baby may get damaged due to an abnormal growth of blood vessels in the retina that can cause irregular bleeding. This condition is called retinopathy of prematurity or ROP. This can cause formation of scar tissues that leads to vision damage.
Jaundice
This is the most common challenge that premature babies face as four out of five babies develop jaundice. This happens when red blood cells break down and produce high levels of bilirubin and the liver is unable to process this. After diagnosis doctors administer phototherapy when the baby is kept under a special light that causes bilirubin to break down.
Gut Problem
A gut disorder called necrotizing enterocolitis or NEC can also happen to babies born prematurely. Common symptoms of this are vomiting, diarrhea, swollen tummy and loss of appetite. Nutritional drips are usually provided to babies suffering from NEC.